Agenda
MRP - Material Requirements Planning
Today I would like to explain what is MRP, and how we run MRP, and what happens. MRP means Material Requirements Planning. Not market risk premium, by the way.(just information for Finance people)
When we run MRP, it is planned how we are going to handle requirements for materials, or shortage of required material stock on hand.

To determine the shortage, we use requirements and safety stock as stock which should be prepared. In addition to that, we use firmed receipts, firmed planned order, and stock on-hand as stocks already planned.
- Safety stock: Stock to be kept at warehouse anytime
- Requirements: stock to be issued from warehouse, or stock to be prepared at warehouse, including following transactions
- Sales order, as a stock to be issued to customer
- Stock transfer order, as a stock to be issued to other warehouse
- Production order, as stock to be consumed for production
- Reservation, as stock to be issued for various reason (scrap etc...)
- Firmed receipts: Stock which would be coming to warehouse, represented by purchase order
- Firmed Planned Order: Stock which would be planned to come to warehouse (Planned order is converted to Production order or Puchase requisition)
- Stock On-Hand: Stock which are available for use
Material shortage is calculated by below formula, and for this, MRP will generate transaction data to fulfill the stock shortage.
Material Shortage = Requirements + Safety Stock - Firmed Receipts - Firmed Planned Order - Stock on-hand
Transaction data generated by MRP would be planned order. This planned order means, "The material needs to be prepare anyway". Planned order would be converted into purchase requisition, if the material in short is those which should be procured from external supplier. On the other hand, if the material in short is defined as in-house production material, planned order would be converted to production order.
Total/Single and Single-Level/Multi-Level
Planning in MRP can be separated into 2 types. Total planning and single-item planning. Total planning will run MRP for plant level, not only for single material. As you can imagine, single-item planning will run MRP for only one material.
In addition, single-item planning has 2 levels. Single-level planning and multi-level planning. Single-level planning will run MRP only for the material and won't run MRP for the component parts. In other words, single-level planning will not explode BOM for the material planned.
On the other hand, multi-level planning will run MRP not only for the material but also the components parts, by BOM explosion.
Total planning would be possible with Tr-code: MD01, and Single Planning would be possible with Tr-code: MD02.
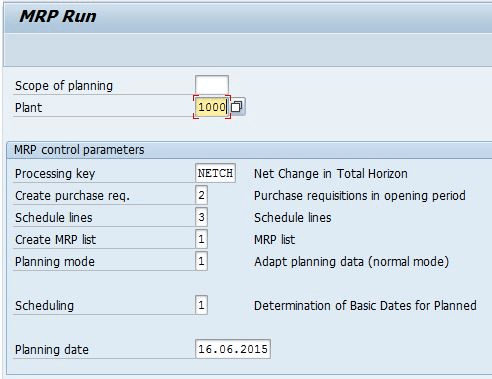
MRP Parameter
To control the behavior of running MRP, several parameter could be useful. These parameter can be selected in a screen to run MRP. (Tr-code: MD01, or MD02)
- Processing Key :
Planning type selected from following- regenerative planning
- net change planning within the total horizon
- net change planning within the planning horizon only
- Create Purchase Requisition and Scheduling Agreement Schedule Lines:
Identifier to determine whether or in which period purchase requisitions and schedule lines are required as a result of the planning run - Create MRP List:
Identifier to determine whether the planning run is to create MRP lists - Planning mode:
Identifier to determine whether the existing planning data is adjusted and the BOMs and task lists re-exploded or whether planning is started again from scratch
Planning horizon - Scope of planning
Planning horizon is a scope of planning activity, or time period that the running MRP should cover. The planning horizon must at least include the time period in which sales orders are received.
For example, let's say our customer sends firm order to us stating delivery due date as 30 days later. If the planning is executed with 20 days as planning horizon, the order from customer won't be handled as requirements yet. It's because, our planning would only cover requirements within 20 days.
10 days later, the order would be captured as requirements and will be target of MRP planning.
The planning horizon is customized for plant or MRP group level.
MRP group and Material group
MRP group is a group which defines how MRP should be run, for certain group of material. In Material Master, there is a Material group, which is used to identify the similar group of material, and this Material group is assigned to the MRP group. So, the planning horizon assigned to one MRP group, would be applied to those materials which are assigned to the Material group, which has linkage with the MRP group.

Processing key
First option in processing key is a regenerative planning. If you choose regenerative planning, MRP will plan all the materials in a plant. For the first run, or planning as day-to-day plant operations when data consistency cannot be guaranteed due to technical errors, this is useful.
There are cases that executing MRP for only those material which has MRP-relevant change is recommended. For example, goods issues, new sales orders, and changes to the BOM structure are occured for certain material in a middle of a day, it would be much faster and reasonable to execute MRP for those material, but for all the materials.
To run MRP for specific material, you will choose single-item planning, and you can also have options in processing key, net change planning (NETCH) or net change planning in the planning horizon (NETPL).
With net change planning , MRP will consider all the MRP relevant changed, and with net change planning in the planning horizon, MRP will only take into account MRP relevant changes that are within the planning horizon.
Create Purchase Requisition /
Scheduling Agreement Schedule Lines
When you run MRP (Tr-code: MD01, or MD02), you can choose which transaction data should be created as a result of MRP run. Possible option is purhcase requisition and schedule lines in scheduling agreement, and you can also set some parameter for the transaction data creation.
First we should check what are purchase requisition and scheduling agreement. Essentially, both of the purchase requisition and schedule lines in scheduling agreement are the same, but the their document structure are different.

Both of the purchase requisition and schedule lines in scheduling agreement are the same, for the point that they are documents to requesting purchasing something.
The difference is, schedule agreement is based on agreement between company and supplier for certain term, and it has assumption that it would be continuously maintained.
As a result, when you select creating Purchase requisition when running MRP, Purchase requisition would be newly created every time. However, when you select schedule lines in scheduling agreement, new schedule lines are added in existing scheduling agreement.
It depends on the scenario or business requirements, but at this moment, let me explain like above.
Create MRP List
The MRP list displays the result of the last planning run. You can determine whether an MRP list should be created during the planning run, when you execute MRP.
MRP list shows how many material are planned as a result of MRP, and you can see similar formatted information as Stock/Requirements list with Tr-code: MD04.
Stock/Requirements list shows the overall status of stocks and future incoming plan, which are based on transaction data generated by MRP.
Planner can compare the 2 lists and to check the changes which has taken place after the MRP run. By comparing the 2 lists, planner can get information for decision making such as whether the MRP running schedule should be more frequent or less frequent.
Review in the end of post
MRP is a important process for manufacturing company, but this is a purely based on firm requirements. In other words, there is no strategic decision in the planning as a result of MRP run.
That is why there are job description with higher salary called as planner, whose mission are to review stocks, requirements, and planning status and to update the planning to satisfy the actual business needs.
This activity was purely based on knowledge and experience of the planner, long ago, however, now there are strong tools to support these planner activity with forecasting tool. SAP now has IBP: Integration Business Planning, or former SPP: Service Parts Planning, and PTC has SPM: Service Parts Management.
In future, I would like to take these forecasting tool also in my blog.